
Dr. S. Sathish Babu
MBBS, MD . Professor & HOD
Overview
The Department of Radiodiagnosis, commonly known as the Radiology Department, plays a pivotal role in modern healthcare by utilizing advanced imaging techniques to diagnose, monitor, and guide the treatment of a wide range of medical conditions. The department’s primary objective is to provide accurate internal images of the body, aiding clinicians in precise diagnosis, effective treatment planning, and continuous monitoring of disease progression. Radiodiagnosis is integral to nearly all medical specialties, serving as a cornerstone for both preventive and curative healthcare practices, and enabling advanced treatment procedures with accuracy and confidence. The department is equipped with modern imaging modalities operated by skilled radiologists and technologists to ensure high-quality results. It emphasizes patient safety, timely reporting, and adherence to established imaging protocols. Through continuous technological upgrades and expertise, the department supports comprehensive, patient-centered clinical care.

Overview
The Department of Radiodiagnosis, commonly known as the Radiology Department, plays a pivotal role in modern healthcare by utilizing advanced imaging techniques to diagnose, monitor, and guide the treatment of a wide range of medical conditions. The department’s primary objective is to provide accurate internal images of the body, aiding clinicians in precise diagnosis, effective treatment planning, and continuous monitoring of disease progression. Radiodiagnosis is integral to nearly all medical specialties, serving as a cornerstone for both preventive and curative healthcare practices, and enabling advanced treatment procedures with accuracy and confidence. The department is equipped with modern imaging modalities operated by skilled radiologists and technologists to ensure high-quality results. It emphasizes patient safety, timely reporting, and adherence to established imaging protocols. Through continuous technological upgrades and expertise, the department supports comprehensive, patient-centered clinical care.

Dr. S. Sathish Babu
MBBS, MD . Professor & HOD
Overview
The Department of Radiodiagnosis, commonly known as the Radiology Department, plays a pivotal role in modern healthcare by utilizing advanced imaging techniques to diagnose, monitor, and guide the treatment of a wide range of medical conditions. The department’s primary objective is to provide accurate internal images of the body, aiding clinicians in precise diagnosis, effective treatment planning, and continuous monitoring of disease progression. Radiodiagnosis is integral to nearly all medical specialties, serving as a cornerstone for both preventive and curative healthcare practices, and enabling advanced treatment procedures with accuracy and confidence. The department is equipped with modern imaging modalities operated by skilled radiologists and technologists to ensure high-quality results. It emphasizes patient safety, timely reporting, and adherence to established imaging protocols. Through continuous technological upgrades and expertise, the department supports comprehensive, patient-centered clinical care.
Dr. S. Sathish Babu
MBBS, MD . Professor & HOD
Professor & HOD
Mission
To deliver accurate, timely, and safe diagnostic imaging services using advanced technology and expert interpretation to support precise clinical decision-making.
Faculties
| S.No | Name | Designation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dr. S. Sathish Babu | Professor |
| 2 | Dr. Vinod Sukumaran | Professor |
| 3 | Dr. Rohit R Chennithala | Associate Professor |
| 4 | Dr. Bharath Chandran G | Assistant Professor |
| 5 | Dr. Najla P | Assistant Professor |
| 6 | Dr. O C Assvath | Assistant Professor |
| 7 | Dr. Jenish Radhakrishnan Sumathi | Assistant Professor |
| 8 | Dr. Vivek Kumar A S | Senior Resident |
| 9 | Dr. Jobin Mathew Jose | Senior Resident |
| 10 | Dr. Renees Thajudeen | Senior Resident |
| 11 | Dr. Siddharth Rupak S | Senior Resident |
| 12 | Dr. Linda Sherin G | Senior Resident |
| 13 | Dr. VISHNU SANKAR T S | Senior Resident |
| 14 | Dr. SUNILNITHI K | Junior Resident |
| 15 | Dr. Priyadharshini C | Junior Resident |
| 16 | Dr. Revanth | Junior Resident |
| 17 | Dr. Varshini V.M | Junior Resident |
| 18 | Dr. Roshan Shaji | Junior Resident |
| 19 | Dr. Avni S Kumar | Junior Resident |
| 20 | Dr. Sylviya Charles | Junior Resident |
| 21 | Dr. Dharshika Retna Sigamony | Junior Resident |
| 22 | Dr. Padmanaban | Junior Resident |
| 23 | Dr. Antlin Sushma Lysander | Junior Resident |
| 24 | Dr. Jevanish Nijin V H | Junior Resident |
| 25 | Dr. Dayaakar R | Junior Resident |
| 26 | Dr. Priyanka P S | Junior Resident |
| 27 | Dr. Rajashree.N.S | Junior Resident |
INFRASTRUCTURE
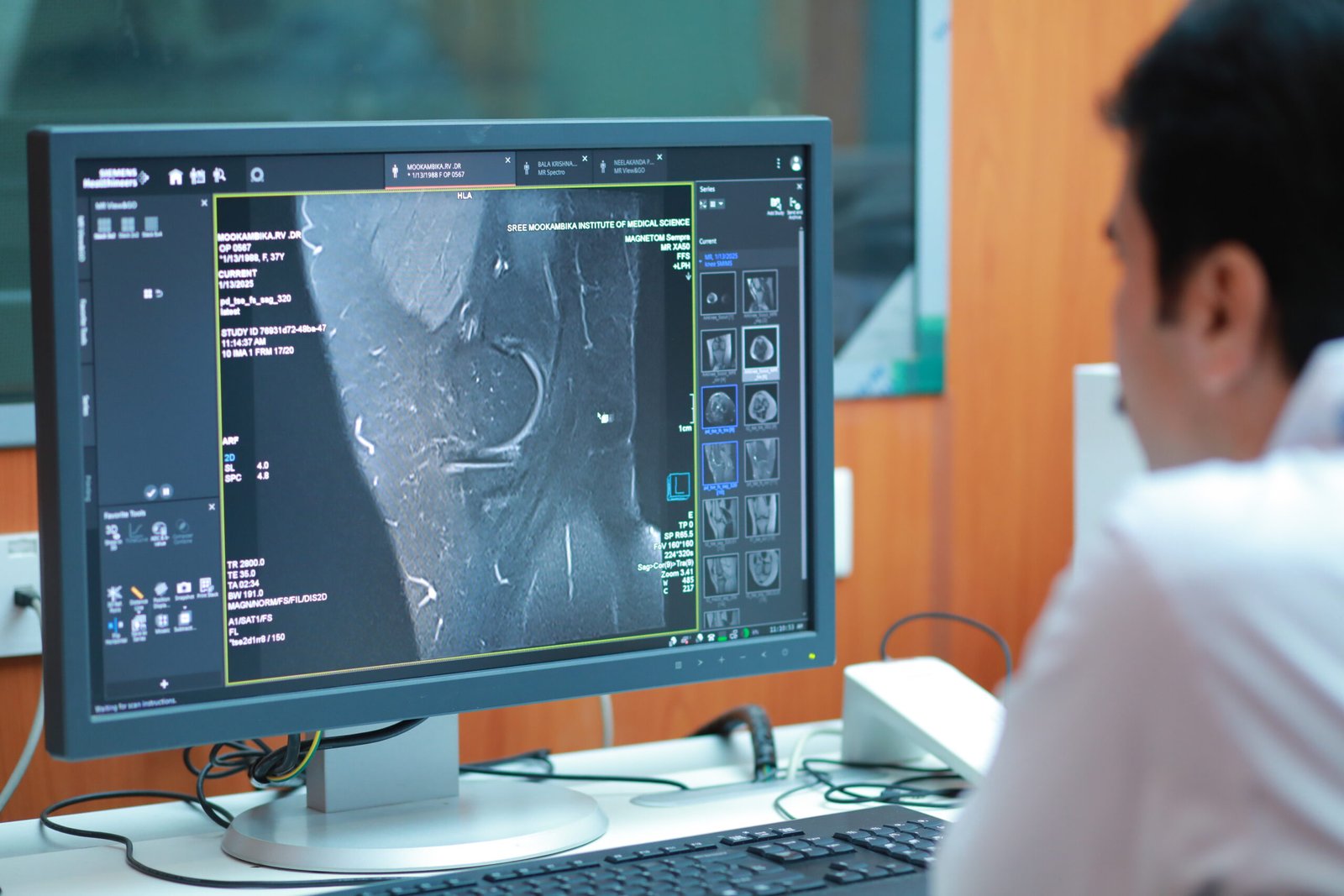

The Department of Radiodiagnosis plays a vital role in modern healthcare by providing advanced imaging for disease diagnosis, evaluation, treatment planning, and patient monitoring, supporting nearly all medical specialties. The facility ensures patient comfort and safety with a spacious reception area, separate preparation rooms, and dedicated imaging rooms for X-ray, CT, MRI, Ultrasound, Mammography, along with control rooms, organized storage, and emergency-ready imaging areas for trauma and critical care. A comprehensive range of services is offered, including X-rays, CT scans, MRI, Ultrasound/Doppler, Mammography, Nuclear Medicine, with specialized support from fluoroscopy and interventional radiology for minimally invasive procedures such as biopsies, drainages, and stent placements. The department has experienced faculty who provide academic mentorship and foster research in areas like Cardiac CT and Interventional Radiology, while promoting strong collaboration with clinical specialties. With high-quality UG and PG teaching programs, multiple research publications, conference recognitions, community screening initiatives, and continuous training under CBME, the department continues shaping the next generation of radiologists.
- Reception and Waiting Area: A spacious, comfortable waiting area with adequate seating for patients. It should be equipped with information about procedures and expected waiting times.
- Patient Preparation Rooms: Private rooms for changing into hospital gowns, and pre-procedure preparation (especially for procedures like MRI, CT scans, and interventional radiology).
- Radiology Rooms: Dedicated rooms for each imaging modality (X-ray, CT, MRI, Ultrasound, etc.). These rooms must be designed to ensure safety, privacy, and ease of access.
- Control Rooms: Separate control rooms equipped with computers and monitors for technicians and radiologists to operate and monitor equipment during imaging procedures.
- Storage Areas: Proper storage for imaging films, digital storage, contrast agents, patient records, and other diagnostic materials.
- Emergency Facilities: Provisions for emergency cases, such as trauma bays for X-ray and CT scanning, as well as direct access to intensive care units (ICU) or operating rooms in case of critical conditions.
1. SPECIALITY SERVICES
Imaging Services
X-ray: One of the most common imaging techniques, used for assessing bones, joints, chest, and other structures.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional images, especially useful for complex cases involving the brain, abdomen, and chest.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images, particularly for soft tissues such as the brain, spinal cord, and muscles.
Ultrasound (USG/Doppler): Uses sound waves to create images, commonly employed for monitoring pregnancies, abdominal organs, and blood flow studies.
Mammography: A specialized X-ray technique to examine the breasts and detect early signs of cancer.
Nuclear Medicine: Involves the use of small amounts of radioactive material to diagnose and treat diseases, often applied in cancer, bone disorders, and thyroid evaluations.
Speciality Services
Fluoroscopy: Continuous X-ray imaging that provides real-time visualization of internal structures, commonly used during interventional procedures such as catheter insertions and gastrointestinal studies
2.PROCEDURE
Interventional Radiology (IR): A subspecialty of radiology that performs minimally invasive procedures—such as biopsies, drainage, and stent placements—under imaging guidance using CT, ultrasound, or fluoroscopy.
3. POST GRADUATE PROGRAMMES/ FELLOWSHIPS
MD –Radiodiagnosis
4. CMEs, CONFERENCES, WORKSHOPS, SEMINARS DONE IN THE DEPARTMENT
Interdepartmental Meetings and Seminars
5. MERITS AND OTHER ACHIEVEMENTS
Strengths of the Department
Experienced Faculty: Highly qualified and experienced faculty members provide expert guidance and mentorship to students and researchers.
Diverse Research Areas: Specialization in multiple areas of Radiology, including Cardiac CT and Interventional Radiology, offering wide-ranging research opportunities.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Active collaboration with other departments fosters innovative research and knowledge exchange.
Educational Excellence: High-quality undergraduate and postgraduate programs prepare students for successful careers in academia, industry, and healthcare.
Achievements
Publication of Research Papers: Faculty and students publish in prestigious scientific journals, contributing to advancements in Radiology.
Awards and Recognition: Postgraduate students receive awards and recognition for best paper presentations and research contributions in academic conferences.
Community Outreach: Faculty and postgraduates participate in medical camps, educating the public and providing benefits through screening X-rays, mammograms, and ultrasounds.
Training and Mentorship: Ongoing training and mentorship on CBME (Competency-Based Medical Education) and research, nurturing the next generation of medical professionals.
